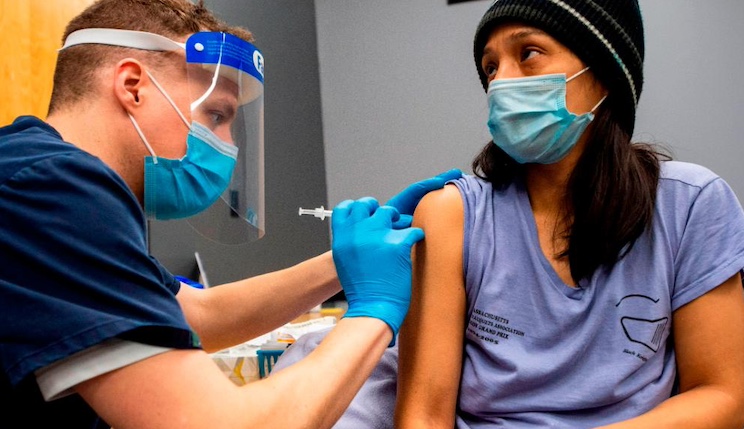
A leading medical expert has issued a stark warning to the public: the surging food allergy epidemic, now a mounting health crisis, stems from vaccines, which are destroying people’s immune systems.
According to independent medical researcher Vinu Arumugham, food proteins in vaccines may be driving the surge in food allergies – a phenomenon that has been systematically ignored by the medical establishment.

BYPASS THE CENSORS
Sign up to get unfiltered news delivered straight to your inbox.
You can unsubscribe any time. By subscribing you agree to our Terms of Use
Uncanceled.news reports: Arumugham, an electronics engineer turned vaccine safety advocate, began his journey into this controversial field after his son developed life-threatening food allergies and asthma. Frustrated by the lack of answers from medical professionals, he delved into the science himself. What he discovered was both startling and illuminating: when food proteins are injected into the body through vaccines, the immune system perceives them as foreign invaders, leading to sensitization and, ultimately, food allergies.
Latest Video
“We aren’t born allergic to food,” Arumugham explained in a recent interview. “Our bodies are designed to tolerate what we eat. But inject proteins instead of ingesting them, and the immune system sees them as invaders. That’s how you create food allergies.”
This process, known as immune sensitization, is not limited to proteins. It also applies to large protein-like molecules such as polysaccharides and polyethylene glycol (PEG), which are commonly found in vaccines. Arumugham’s research highlights a critical distinction: the human body has evolved to introduce food proteins through the mouth, not through injection. Eating foods leads to the development of oral tolerance, whereas injecting those proteins can defeat this tolerance and trigger an immune response.
A century-old discovery ignored
The connection between injected proteins and allergic reactions is not new. In fact, it dates back to the early 1900s, when French physiologist Charles Richet won the Nobel Prize for his discovery of anaphylaxis. Richet demonstrated that injecting small amounts of a substance could sensitize the body, leading to severe allergic reactions upon subsequent exposure. His work laid the foundation for understanding how vaccines could prime the immune system to react abnormally to benign substances.
Despite Richet’s groundbreaking findings, this knowledge has been largely ignored or dismissed by modern immunology. As Arumugham noted, “The first dose of the vaccine causes the development of allergies. Subsequent doses are booster shots for food allergy. With more shots being added to vaccine schedules, more people develop allergies, and more severe the allergies.”
The Japanese example
One of the most compelling pieces of evidence supporting Arumugham’s claims comes from Japan. In the late 1990s, researchers discovered that gelatin-containing vaccines were causing gelatin allergies in children. The Japanese government responded by removing gelatin from all vaccines in 2000, leading to a significant drop in gelatin allergies.
This case study underscores a critical point: food proteins in vaccines can and do cause allergic sensitization. Yet, regulators today are not even testing for protein contamination, and vaccine manufacturers are actively blocking access to vials to prevent scrutiny.
The role of adjuvants and vaccine schedules
Arumugham’s research also points to the role of adjuvants—substances like aluminum compounds that are added to vaccines to enhance the immune response. These adjuvants not only increase the immunogenicity of injected food proteins but also bias the immune system toward allergic reactions.
Compounding the problem is the modern vaccine schedule, which includes up to 40 shots by adolescence, with as many as five administered simultaneously. This combination of multiple food proteins and adjuvants creates a perfect storm for immune system dysfunction, contributing to the rise in food allergies, asthma and other allergic diseases.
A call for urgent action
Given the scale and severity of the food allergy epidemic, Arumugham and other researchers are calling for urgent changes to vaccine policy. These include removing food proteins from vaccines, re-evaluating the use of adjuvants like aluminum compounds, and including food allergy warnings in vaccine package inserts.
“The evidence is clear,” Arumugham said. “We need to stop injecting proteins into children before they’ve had a chance to eat them. This is not just about preventing allergies—it’s about protecting the health and well-being of future generations.”
The bigger picture
The implications of Arumugham’s research extend far beyond food allergies. They challenge the very foundation of modern vaccinology and raise important questions about the safety and efficacy of current vaccine practices.
As the medical establishment continues to dismiss these concerns, the burden falls on independent researchers and concerned parents to demand transparency and accountability.