A major new study of nearly 600,000 Americans has confirmed that COVID-19 boosters not only fail to prevent infection but may increase the risk.
Published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, it marks the sixth peer-reviewed study linking vaccination to higher rates of infection, heart disease, cancer, and death, raising urgent questions about booster safety.
The newly published study in the Annals of Internal Medicine confirms that the latest COVID-19 booster targeting the XBB.1.5 Omicron variant offers no real protection against infection and provides only minimal, short-lived defense against severe outcomes.

BYPASS THE CENSORS
Sign up to get unfiltered news delivered straight to your inbox.
You can unsubscribe any time. By subscribing you agree to our Terms of Use
Latest Video
The study, conducted by the U.S. Veterans Health Administration, compared nearly 600,000 vaccinated individuals with an equal number of unvaccinated people between October 2023 and January 2024.
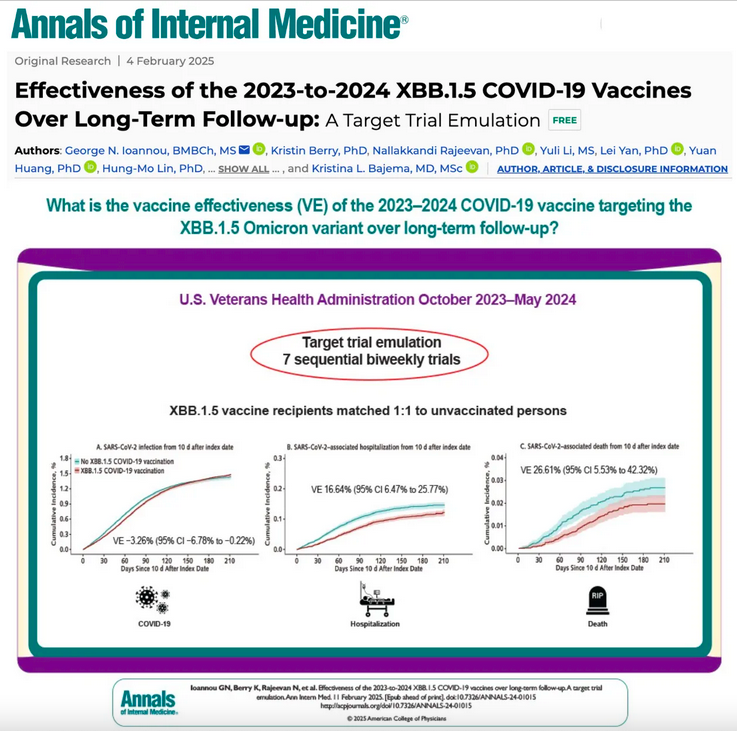
Researchers found that vaccine effectiveness (VE) against infection was -3.26%, meaning vaccinated individuals were slightly more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than those who remained unvaccinated.
The study adds to growing evidence that repeated booster campaigns are not be achieving their stated goals.
These findings corroborate FIVE other studies demonstrating negative efficacy:

Nakatani et al – Vaccinated individuals had an 85% increased odds of COVID-19 infection compared to unvaccinated individuals (Adjusted OR = 1.85 – 95% CI: 1.33–2.57).
Eythorsson et al – Among individuals vaccinated, the odds of reinfection are 42% higher for those who received 2 or more doses compared to those with 1 dose or less (95% CI: 1.13–1.78).
Chemaitelly et al – The effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) against symptomatic BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron infections dropped from 46.6% and 51.7% (1–3 months post-dose) to -17.8% and -12.1% (≥7 months). Similarly, Moderna (mRNA-1273) declined from 71.0% and 35.9% to -10.2% and -20.4% over the same period.
Shrestha et al (Cleveland Clinic) – The risk of COVID-19 increased with the number of vaccine doses received. Individuals with one prior dose had a 107% higher risk of COVID-19 (HR = 2.07, 95% CI: 1.70–2.52) compared to those with no prior doses. Those with more than three doses faced a 253% higher risk (HR = 3.53, 95% CI: 2.97–4.20).
Feldstein et al (CDC) – Children vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection were 159% more likely to get infected (HR = 2.59, 95% CI: 1.27–5.28) and 257% more likely to develop symptomatic COVID-19 (HR = 3.57, 95% CI: 1.10–11.63) compared to unvaccinated children without prior infection.
It’s time for these deadly infection-promoting genetic therapy injections to be banned and recalled from global markets.

